The Hidden Dangers of Obesity: How Excess Weight Affects Your Body

Author: Chika Jones, RN, RM, RPHN, BNSC
Reviewed by: Azuka Ezeike, MBBS, FWACS, FMCOG, MSc (PH)
Introduction
Did you know adult obesity has doubled globally since 1990? In 2022, up to 890 million people were found to be living with obesity [1].“Obesity is a chronic or non-communicable disease and is identified as the fifth reason for Global mortality”[2]. Obesity, as defined by the World Health Organization(WHO), is excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health[1]. It impacts physical health as it leads to increased risk of diseases like:
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Musculoskeletal disease(diseases of the bone and muscles)
- Cardiovascular(diseases of the heart and blood vessels [3].
- Mental health problems: People with obesity often face stigma and discrimination. This predisposes them to mental health problems like depression, anxiety, depression and reduced quality of life [4].
In this article, we will learn how obesity affects physical, emotional, mental and other aspects of health. We would also consider the practical tips one can use to manage obesity and its health risks.
The difference between obesity and overweight
Obesity and overweight are used interchangeably but are different.To Understand the difference between them we have to discuss the tools used to assess obesity and overweight.
Two tools are used. These are Body Mass Index (BMI) and Waist to Hip Ratio (WHR).
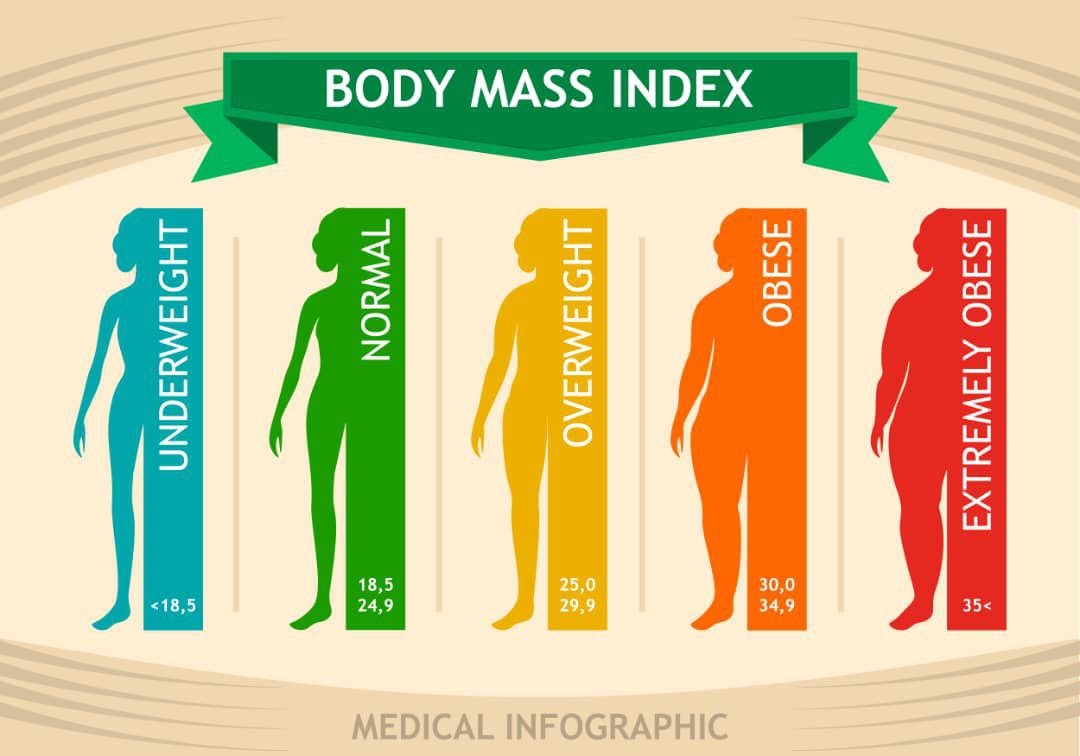
The most common tool for the assessment of obesity or overweight is BMI. Body Mass Index is calculated by your weight and height [1].
BMI= Weight (Kg)/ Height ().
The normal BMI is between 18.5 to 24.9. Overweight is diagnosed when the BMI of an individual is 25.0 to 29.9 while obesity is when an individual has a BMI of 30 and above [5].
The Physical Health Risks of Obesity
Obesity is linked to various diseases that can affect physical health. We will discuss this as we go along.The common diseases include:
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Metabolic Disease
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease that affects obesity include:
- Hypertension: Increase in the pressure of blood flow in the blood vessels(arteries)
- Heart failure: It is a chronic condition also referred to as congestive heart failure. The heart is weak and unable to pump blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Heart attack:It is known as myocardial infarction. When the blood flow to the heart is blocked and results in a damaged heart muscle.
- Venous thromboembolism: This disease occurs when blood clots (thrombus) that form in the blood vessels break loose and travel to another blood vessel.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart. CAD occurs when cholesterol builds up and blocks the arteries.
- Atherosclerosis: Excess body fat leads to higher levels of "bad" cholesterol(fat). This leads to the buildup of fat in the arteries(blood vessels) causing them to narrow.
Metabolic Disease
Metabolic health deals with how food is converted to energy and its utilization in the body[6]. Obesity may cause a change in the way some hormon work.. This affects the way the body converts and utilizes food; hence why obesity is linked to metabolic health disorders [7].
One of the metabolic health disorders obese individuals are prone to is type 2 diabetes mellitus [8]. In normal metabolic health conditions, food is broken down into glucose to be utilized by the body cells to provide energy. The insulin hormone must be available for this to take place [9].
People with type 2 diabetes mellitus produce “the hormone” insulin. The body's cells cannot use it effectively as a result of insulin resistance, obesity is a major contributor to insulin resistance [10]. Though it is uncertain how insulin resistance and obesity are related, evidence shows that adipocytes (fat cells that store energy) secrete some factors that may reduce insulin sensitivity to the cells [11]. However, not all people with insulin resistance are obese [12].
Joint and Musculoskeletal Issues
- Osteoarthritis: It is a breakdown of the cartilage in the joints leading to friction between the bones. Cartilage is a tissue that connects bones to form a joint.
Musculoskeletal issues like osteoarthritis related to obesity can occur due to extra pressure from daily activities of living like walking, running, and bathing. This pressure can affect weight-bearing joints in the knees, hips, and ankles and predisposes them to osteoarthritis [2]. This pressure also affects the spinal column causing severe back pain and may significantly affect the individual's flexibility and may lead to fibromyalgia [8].
Other Health Risks
There are other risks people with obesity are predisposed to such as
- Cancers
- Respiratory problems
- Infections
- Reproductive problems
- Skin diseases
- Gallbladder disease
- Fatty liver
Cancers
Research shows that obesity puts one at risk of:
- Endometrial cancer(cancer of the womb)
- Breast cancer after menopause
- Colorectal cancer(cancer of the large intestines)
- Renal cancer( cancer of the kidneys) [3].
- Hodgkin's disease ( cancer of the lymphatic system)
- Ovarian cancer( Cancer of the egg-producing organ in females
- Cancer of the gallbladder
- Cancer of the pancreas
Respiratory diseases
Respiratory diseases, such as sleep apnea, are often linked to obesity. Sleep apnea is characterized by loud snoring at night, followed by daytime sleepiness. In severe cases, individuals may experience brief periods of stopped breathing, followed by resumed breathing. Obesity is a significant risk factor for sleep apnea and other respiratory diseases [2].
Reproductive problems
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) A disease associated with irregular periods and infertility in women. Though it is not caused by obesity, the symptoms are worsened by obesity[2]. It is a risk factor for infertility for men and women [10].
- Gestational diabetes ( Diabetes that occurs during pregnancy).
- Preeclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy).
- High risk of miscarriage[12].
Skin Diseases
- Skin dryness
- Skin erythema (Redness of the skin).
- Intertrigo( an Inflammatory condition caused by skin-to-skin friction and heat. It typically occurs in the groins, under the breast and arms, and between the toes [13].
Gallbladder Diseases
Gallbladder disease is any disease condition that affects the Gallbladder. The Gallbladder is an organ found in the digestive system (stomach ). The main function of the gallbladder is to store bile produced by the liver. This bile helps to break down fats and fat-soluble vitamins (A,D,E &K).
One disease condition that causes gallbladder disease is gallstones. Gallstones are lumps of stones, made from cholesterol that forms in the gallbladder. Obesity is seen as one of the predominant causes of gallstone formation [11]. The relationship on how obesity causes gallstone is not fully understood. However, precipitation of cholesterol within the bile is involved (Cholesterol is abundant in the bile, it becomes solid as stone and eventually creates gallstones) [11].
Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is also referred to as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). It occurs when excess fat builds up on the liver cells. inflammation, scarring and liver damage occur. It is usually seen in obese individuals [14]
Infections
- Urinary tract Infection (UTI): it affects the renal system (kidneys, bladders etc.). Studies show a high prevalence of UTI on obese individuals. Due to the excess weight placed on the bladder (storage for urine). Urine stores longer than usually and causes bacteria to grow[15].
- Candidiasis: It is a fungal infection caused by overgrowth of candida albicans (yeast) in the body . It is highly prevalent in obese people and causes other infections like folliculitis (hair follicle over all or part of your body are infected), furunculosis (boils on the skin), or paronychia (skin around the nails is infected) of the hands or feet [15].
The Emotional and Mental Health Impact of obesity
Individuals with obesity are faced with:
- Depression.
- Anxiety disorders.
- Low self-esteem.
- Negative eating habits.
- Social stigma and isolation.
Anxiety disorder symptoms are associated with excess fear and worry[16]. Individuals with obesity also have a higher risk of depression and anxiety levels. This leads to a poor quality of life that may result in negative eating attitudes thus worsening obesity [17].
Negative eating attitudes could be seen as emotional eating, where one eats more when they are in a bad mood. Depression could cause one to be an emotional eater causing excess weight. Emotional eating can occur regardless of depressive symptoms [17]. Social stigma against obesity decreases self-esteem and worsens obesity [17]. It increases the risk of anxiety, depression, and chronic stress. It also prevents individuals from seeking professional help or participating in physical activities due to fear of humiliation or judgment.[18].This leads to loneliness and isolation for obese individuals, significantly harming both their mental and physical health. [17].
We have gained an understanding of what obesity is and its impact on health, which is beneficial. However, what practical tips can we follow to manage obesity and reduce health risks?Read more to find out.
Practical Tips for Managing Obesity and Health Risks
- Excess weight is burned off by being active. Lack of exercise is not a direct cause of obesity, but regular physical activity can help manage it. [12].
A good way to shed excess weight is through exercise, which also helps maintain good muscle tone. Even a 30-minute walk, jog, or run can make a difference.[5].
- Make healthier food choices by eating fruits, vegetables and whole-grain carbohydrates. Avoid fat, processed and candied foods (fruits that are covered in heated sugar syrup to preserve it). They give empty calories (contain sugars but have no nutritional value) [19]. Support by a dietician may be needed. [8].
- Ensure to seek treatment from your healthcare provider if you have diseases like hypothyroidism, Cushing syndrome and PCOS which are associated with obesity [5].
- Another practical tip to manage obesity is stress management. This is because stress releases hormones like cortisol which directly relate to obesity development. Glucocorticoid hormones regulate how much fat is stored in specific areas of the body. It also increases appetite which causes one to be an emotional eater [19]. This could lead to excess weight. Proper sleep and effective stress management help to reduce weight [2].
Conclusion
Obesity is a public health issue that affects the physical and mental health of individuals. It is important to take practical steps and develop healthy lifestyle choices to improve the quality of life. What steps would you be willing to take to manage obesity and seek a healthy lifestyle?
References
1.World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight [Internet]. World Health Organization. WHO; 2024. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight 2.Mohajan D, Mohajan HK. Obesity and Its Related Diseases: A New Escalating Alarming in Global Health. Journal of Innovations in Medical Research. 2023 Mar;2(3):12–23. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369451854_Obesity_and_Its_Related_Diseases_A_New_Escalating_Alarming_in_Global_Health . 3. Tehreem Riaz, Muhammad Akram, Umme Laila, et al. Causes, risks factors and medical consequences of obesity. IAIM, 2023; 10(8): 39-48. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373272390_Causes_risks_factors_and_medical_consequences_of_obesity4. Dąbrowska J, Wójcik M, Samek I, Jańczyk M, Bator D, Milanowska J. Obesity and mental health. Journal of Education, Health and Sport. 2020 June 26;10(6):199. Available fromhttps://www.researchgate.net/publication/343313354_Obesity_and_mental_health 5.Vijay. J, Natarajan. P, Gokul. V, Janani. A.M, Mumthaj. P. A Global Review of Obesity. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research [Internet]. 2021 May 15;68(1). Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352952203_A_Global_Review_of_Obesity 6. Zinn C. Metabolic health: A new frontier. Journal of Metabolic Health . 2023;6(1):2. Available from https://journalofmetabolichealth.org/index.php/jmh/article/view/92/292 7. Anand Anbarasu. Obesity: A critical Review. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences [Internet]. 2011 Nov 10;2(4). Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283713137_Obesity_A_critical_Review 8. Yee LC, Adrian CW, Khamki KA, Ying KY, Shahfri MFM, Hee NB, et al. Physical Health Impacts of Obesity: Comprehensive Review. Progress in Drug Discovery & Biomedical Science [Internet]. 2023 Mar 10;6(1). Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369162341_Physical_Health_Impacts_of_Obesity_Comprehensive_Review
9. Ozougwu, Jevas & Obimba, K.C. & Belonwu, C.D. & Unakalamba, C.B.. (2013). The pathogenesis and pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Academic Journals. 4. 46-57. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312716171_The_pathogenesis_and_pathophysiology_of_type_1_and_type_2_diabetes_mellitus 10.Syed QA. Factors Contributing to Obesity and Associated Health Risks. Interventions in Obesity & Diabetes. 2021 Sep 23;5(4). Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372015521_Factors_Contributing_to_Obesity_and_Associated_Health_Risks 11.Ali AT, Crowther NJ. Health risks associated with obesity. Journal of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa. 2005 Jul;10(2):56–61. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273740655_Health_risks_associated_with_obesity 12.Klaudia Kułak, Izabela Sztybór, Katarzyna Kamińska. Obesity - an epidemic of the 21st century – literature review. Journal of Education, Health and Sport. 2024 May 17;70:49557–7. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380686497_Obesity_-_an_epidemic_of_the_21st_century_-_literature_review 13.Frasca D, Strbo N. Effects of Obesity on Infections with Emphasis on Skin Infections and Wound Healing. Journal of Dermatology and Skin Science. 2022;4(3):5–10. Available from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10448872/ 14. 1.NHS . Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [Internet]. NHS. 2022. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease 15.Pugliese G, Liccardi A, Graziadio C, Barrea L, Muscogiuri G, Colao A. Obesity and infectious diseases: pathophysiology and epidemiology of a double pandemic condition. International Journal of Obesity [Internet]. 2022 Mar 1;46(3):449–65. Available from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41366-021-01035-6 16.Wang J, Ran X, Ye J, Deng R, Dang W, Fan Y, et al. Obesity-Associated Anxiety Is Prevalent among College Students and Alleviated by Calorie Restriction. Nutrients [Internet]. 2022 Jan 1;14(17):3518. Available from https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/17/3518
17. Qiang Z. Psychological Factors That Can Impact Obesity and Overweight. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media. 2024 Nov 15;73(1):8–13. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/385923755_Psychological_Factors_That_Can_Impact_Obesity_and_Overweight 18.Segal Y, Gunturu S. Psychological Issues Associated With Obesity [Internet]. PubMed. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Available from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK603747/ 19. Jha AK, Das AK. Obesity: a global health problem. International Journal Of Community Medicine And Public Health. 2019 June 28;6(7):3168. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334099865_Obesity_a_global_health_problem